Configuring WordPress – Basic Structure and Menus
Populating the WordPress website, adding pages, posts, categories and setting up menus.
Pages are static pages that can be edited, but generally remain the same. Pages do not get archived, once edited the old content is overwritten.
Posts are texts that are displayed in a post template ‘page’. They are saved in chronological order and (depending on the theme settings) can be displayed with short intros on a category “home” page. Clicking their ‘read more’ link displays the entire post . Posts are sorted into (already set up) categories. Posts can be searched by category and other identifiers such as date published, author, tags, etc.
Categories: WordPress ships with a default “Un-categorized” category, so before writing posts, it’s important to establish some additional categories to organize the site’s posts. The categories will depend on the content and organization of the site. A post is then assigned to one of the categories as appropriate. If no category is assigned, WordPress will give it the default “Un-categoriesed” category.
Tags: Post also need ‘Tags”. Tags are similar to ‘keywords’, they are words found in the post text, and are usually words that are used in multiple posts. 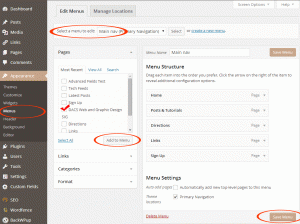
Menu options:
WordPress has a default menu system, and location depends on the theme, however, most themes allow for custom menu(s).
Default menu: When creating a PAGE, WordPress has the option to set the location of the link by numerical order, and whether it’s a sub-link or not.
Custom menus: Custom menus are easy to set up, and allow full control over which and where each page/post/category link appears.
Open the Menu page, under “Appearance”. It will show the location options, depending on the theme. Menu items can be pages, categories, tags, URL’s etc. Select and insert them into the menu, and then drag them into the required order. Options include dragging them ‘offset’ to create a drop-down.
Many themes have additional locations specified for menus. Select which menu you need to edit. When choosing a theme consider how many menu links you’ll have, and whether the theme has enough menu locations built in. Most themes have a main menu and a footer menu, but some have secondary menu’s at the top of the design. A menu can also be used in a widget area.
